LSTM
Long short-term memory LSTM

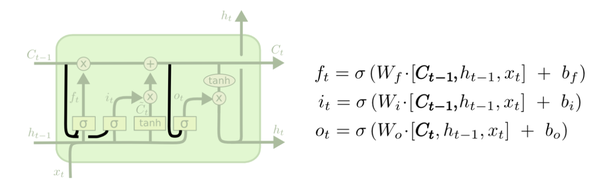
In general, LSTM is like a RNN with a “notebook”to record the information. The pink signs in blocks belongs to the “notebook”, and the yellow ones are gates. Comparing to RNN, LSTM extends the memory of short term information, so it is called long short-term memory.
IDEA: multilayer LSTM: RNN with multi “notebooks”. The first “notebook” record information from RNN outputs; The second “notebook” record information from the first “notebook”… This architecture finally forms a structure with several layers.
A: gradient vanish ELMO Residual Link cansolve this
1. Forget Gate

When the value of sigmoid($\sigma$) varies from 0 to 1, it keeps part of the information and “forget” the other. This is a method to extend the memory of short term memory in “notebook”($C_i$) by balancing the ratio of current information and former information.
2. Input Gate (Update Gate)


Update the information in “notebook”($C_{t-1}$)
3. Output Gate

At last, LSTM uses the record of $C_t$ (updated notebook), and current input ($x_t$) to generate output.
4. Peephole
Both $h_t$ and $C_t$ input into gates.
5. Bi-LSTM

Two LSTM network do not share parameters. Bi-LSTM can consider context-based information instead of former information.



